☝️ The most important facts in brief
- Diabetology is the speciality of human medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus.
- There are different forms of diabetes, which require a correspondingly different approach.
- Diabetology is a branch of internal medicine. The specialist training programme here lasts 6 years.
📖 Table of contents
A diabetologist is a doctor who specialises in the treatment of diabetes. This speciality, diabetology, includes the diagnosis and treatment of various forms of diabetes. Diabetologists work closely with other doctors and specialists from other professions to ensure the best possible care for patients. In this article, you will learn all about the tasks of a diabetologist, the training required and interesting details about diabetes.
Are you interested in studying medicine?
We will be happy to advise you free of charge about your options for studying medicine, including advice on studying medicine in another EU country, which is fully recognised in Germany.

Together for success - futuredoctor and studying medicine abroad
Would you like to Study medicine abroad and are looking for the most suitable university for you and don't really know where to start looking for a suitable country and a good university? futuredoctor will be happy to support you!
In addition to the Student counselling In addition to selecting the university and accompanying you to the desired on-site appointments, futuredoctor also offers support during the application process and preparation for possible aptitude tests and subsequent orientation at the place of study - right through to finding accommodation! Get your Free information pack!
What does a diabetologist do?
A diabetologist is a medical specialist who specialises in diabetes. The metabolic disease commonly known as "diabetes" cannot be cured, which means that diabetes patients must see their doctor regularly throughout their lives. Accordingly, a good relationship between the diabetologist and their patients is important.
An important focus of the work of a diabetologist is to help patients to control their blood glucose levels so that they remain within a healthy range. This is important for the prevention of secondary damage, which unfortunately often occurs with diabetes.
As a diabetologist, you will also have to deal with various other illnesses and problems that are unfortunately associated with diabetes. You will also diagnose and treat these. You will also provide your patients with information and support so that they can live as well as possible with their illness.
Diagnosis of diabetes
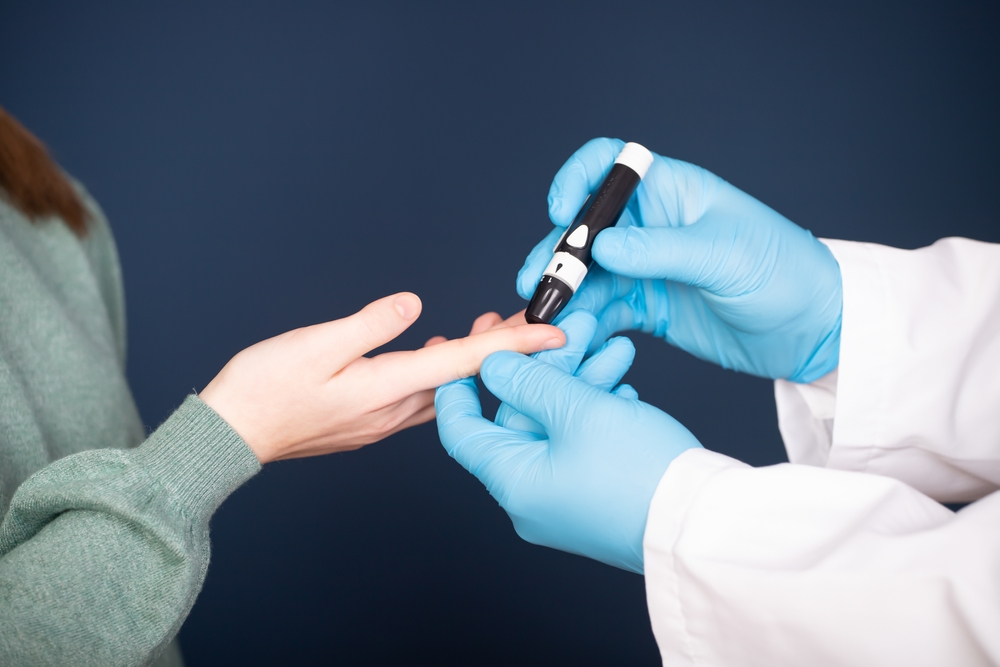
Diabetologists diagnose diabetes using various tests and techniques. These include blood glucose measurements, the glucose tolerance test and the HbA1c test, a blood test to determine haemoglobin associated with glucose.
In endocrinology and diabetology, not only is diabetes itself diagnosed, but the diabetes specialists also categorise which type of diabetes mellitus is involved. This allows the appropriate treatment to be planned together with the patient.
Diabetes mellitus comes in various forms
Not all diabetes is the same. Depending on the type of diabetes, those affected suffer from different consequences and symptoms. It is therefore important for diabetologists to know the different types of diabetes and to plan treatment specifically for each disease.
Diabetes mellitus type 1
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas. Symptoms include elevated blood sugar levels, frequent urination and unexplained weight loss. Specialists in diabetology, internal medicine and endocrinology make the appropriate diagnosis. Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy to keep the concentration of sugar in the blood under control.
Diabetes mellitus type 2
Type 2 diabetes often occurs in people in the second half of life and is therefore also known as adult-onset diabetes. Insulin resistance is usually present, and insulin deficiency due to impaired production of the hormone by the pancreas can also be present.
Symptoms include elevated blood sugar levels, fatigue and frequent urination. The main risk factors include obesity and lack of exercise, which is why type 2 diabetes treatment often centres on close cooperation with a diabetes consultant and lifestyle changes.
Diabetes mellitus type 3
Type 3 diabetes is a rare form of diabetes that occurs in different variants. The diabetologist also monitors the progression of this type of diabetes and develops a treatment that is precisely tailored to the individual diabetic.
Gestational diabetes
This temporary form of diabetes occurs during pregnancy. It is usually diagnosed by means of a glucose tolerance test, which is part of regular antenatal care. The increased blood glucose level in gestational diabetes can affect the baby's growth and usually leads to a very high birth weight, which can be associated with complications at birth. It can also lead to an adjustment disorder in the baby after birth.

Treatment methods in diabetology
Diabetologists and endocrinologists use insulin injections or tablets to treat diabetes mellitus. However, this is not always necessary for all types of diabetes. A change in diet and a healthy lifestyle can often also achieve a lot with type 2 diabetes, for example.
If drug therapy is required, the specialist will tailor it precisely to the needs of the diabetes patient in question.
Therapy with insulin
Insulin therapy is essential in the treatment of type 1 diabetes. The diabetologist monitors this therapy closely and optimises it if necessary. The insulin deficiency is temporarily remedied by the external supply. However, a long-term cure for diabetes is not yet possible, so the therapy must be continued for the rest of the patient's life.
Insulin is also used for advanced type 2 diabetes. Research into new types of insulin and therapeutic approaches is an important area for diabetology specialists.
Nutritional counselling and lifestyle changes
It is extremely important to pay attention to your diet in order to avoid diseases that frequently occur in connection with diabetes, such as nerve damage and circulatory disorders. The diabetologist will therefore also provide detailed advice on this.
Regular exercise and a balanced diet make the management of metabolic diseases much easier, even if it still requires close monitoring and is always a major challenge for the diabetologist and, of course, for those affected.
Training: How to become a diabetologist
To become a diabetologist, you first complete a medical degree. This is followed by specialist training in internal medicine, during which you specialise in endocrinology and diabetology.
During your specialist training, you will have to complete the areas specified in a model training programme and acquire the necessary specialist knowledge about diabetes and related diseases.
Medical studies
The medical degree programme lasts six years and ends with the state examination. Firstly, you will learn the basics of anatomy, physiology and biology required to understand the rest of the programme. This is followed by a clinical phase of the degree programme that prepares you for a career as a doctor, during which you have to complete courses, lectures and examinations in each area.
The clinical part of the degree programme ends with a practical year (PJ). You then take the state examination, after which you can work as a junior doctor on a ward, for example. Your specialisation in diabetology can then begin here.
Training as a specialist in internal medicine and diabetology
The specialist training programme in internal medicine and endocrinology and diabetology lasts 72 months. Diabetologists work in inpatient care for at least 24 months during this additional training.
6 months in the emergency department and 6 months in intensive care medicine are also compulsory. You also have to complete two further specialisms in internal medicine, which you can choose yourself.
The contents of further training to become a diabetologist
Endocrinology, as the "study of the glands of internal secretion", is also a central component of further training to become a diabetologist. You will be taught the following content during your training as a specialist:
- Diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus
- Management of acute illnesses and chronic complications
- Insulin therapy and other treatment methods
- Nutritional counselling and necessary lifestyle changes for diabetes patients
Thanks to the comprehensive training, which usually lasts just as long as the actual medical degree, you will be well prepared for your work as a diabetologist.
Starting signal
What are you waiting for? 🎉
Order your info pack now, find out more about the Studying medicine abroad and get started as a medical student!