☝️ The most important facts in brief
- A cardiac surgeon is a medical specialist who specialises in operations on the heart and the surrounding blood vessels.
- Typical operations in heart surgery include bypass operations, the replacement of heart valves and heart transplants.
- Cardiac surgeons work closely with cardiologists and other doctors to ensure that patients receive comprehensive care.
- To become a cardiac surgeon, you have to study medicine for 6 years and complete 6 years of further training to become a specialist in cardiac surgery.
📖 Table of contents
The cardiac surgery discussed in this article is probably one of the most exciting specialisms in medicine. A cardiac surgeon performs interventions on the heart and must therefore be very familiar with the anatomy of this area. The work is demanding and sometimes involves a great deal of physical and mental strain. In order to become a cardiac surgeon, you have to complete a comprehensive six-year specialist training programme after studying medicine for six years.
Are you interested in studying medicine?
We will be happy to advise you free of charge about your options for studying medicine, including advice on studying medicine in another EU country, which is fully recognised in Germany.
What is a heart surgeon?
Cardiac surgery is the field that specialises in operations on the heart and the vessels in the surrounding area. As the heart is an extremely complex organ, as a doctor specialising in cardiac surgery you need extensive specialist knowledge and good fine motor skills.
Cardiac surgery is a speciality of the Surgery. When performing heart surgery, you work closely with several other specialities and try to restore a great deal of quality of life to those affected and possibly even save their lives through treatment.
Training as a cardiac surgeon
If you are aiming to become a specialist in cardiac surgery, you must first complete the 6-year medical degree programme and graduate with the state examination.
After successfully passing the examination, you can then look for a hospital as an employer and start your specialist training in cardiosurgery. This also takes 6 years and includes, among other things:
- General surgery
- Thoracic surgery
- Vascular surgery
- Cardiology
- Intensive care medicine
- Emergency medicine
By working in different areas during your specialist training, you will gain a comprehensive knowledge of the various diseases that will be relevant to you as a doctor in cardiac surgery and their treatment. You will learn the skills you need to be able to perform cardiac surgery yourself later on.
Whether you acquire the title of "Dr med." during your training and further education is an individual decision. Theoretically, you can also work as a specialist in cardiac surgery without a doctorate, but the "Dr. med." is usually beneficial for your own career and is therefore integrated into your own career path by most specialists.
Cardiac surgery in the clinic: typical heart procedures
In cardiac surgery, you will work with a skilled team to perform a variety of different procedures on the heart, cardiac vessels and in the immediate vicinity of the organ. In addition to the actual procedures, your tasks also include their preparation and follow-up as well as comprehensive diagnostics. We will now introduce you to a few typical heart operations that you will regularly encounter in cardiac surgery.
Bypass
During bypass surgery, a narrowed or blocked blood vessel is bridged by a "bypass" to ensure that the heart is supplied with oxygen. Depending on the extent of the heart operation and the technique used, bypass surgery can be performed on the open heart with the aid of a heart-lung machine or on a closed heart.
Operations on the heart valve
The heart valve serves to prevent the backflow of blood into the venous vessels and thus helps to ensure blood circulation and the supply of oxygen to the body. In the event of injuries or congenital damage to the heart valve, not enough blood can be pumped through the body, the heart is strained and performance is severely restricted.
For the treatment of heart disease, it is sometimes necessary to repair or replace a damaged heart valve. Both mechanical and biological replacement valves are available for this purpose.
Pacemaker implantation
If the rhythm of the heart is disturbed or there is a risk of the heartbeat stopping, the surgeon can implant a pacemaker. This monitors the heart rhythm and regulates it with the help of electrical impulses. Depending on the type of pacemaker, it can be recharged externally or needs to be replaced after around 10 years by another procedure.
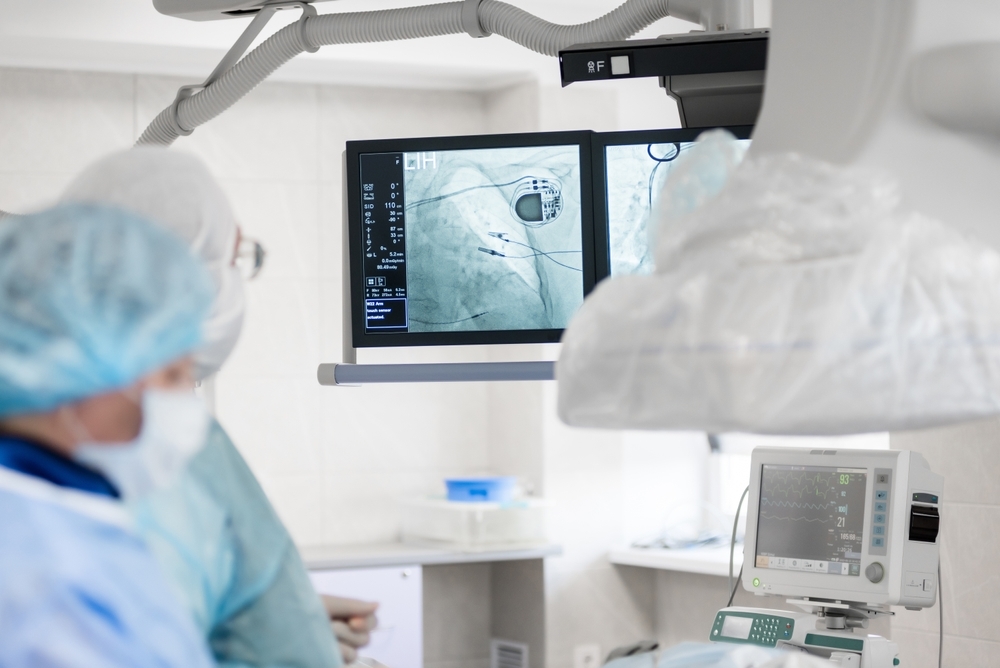
Ablation procedure
This type of operation can be used to treat certain types of cardiac arrhythmia. The heart surgeon cauterises a small area of heart tissue in order to interrupt unwanted signals in this area. The method is minimally invasive, as it can be performed using a cardiac catheter, meaning that the thorax does not have to be opened and the heart-lung machine does not have to be used. It is therefore a comparatively minor procedure.
Heart transplantation
Heart transplantation is one of the most complex procedures in cardiac surgery. Doctors replace a seriously diseased heart that is no longer able to function with a donor heart from a deceased person. Many colleagues work hand in hand during such an operation, and comprehensive and lifelong aftercare is required. The main aim is to prevent the new heart from being regarded by the body as a foreign body and rejected.
The future of cardiac surgery: an outlook
Like all areas of medicine, the speciality of heart surgery is constantly evolving. Thanks to modern techniques, heart surgery can now be performed with high precision. The use of robots can help to minimise injuries during surgery and even highly complex situations can be managed well.
New materials, artificial heart valves and vessels and many other innovative technologies now make it possible to help heart patients who previously had no chance.
What challenges do you face as a heart surgeon?
As a doctor in cardiac surgery, you face major challenges every day. During your work in the operating theatre, you are often at the table for many hours at a time. This is a mental and physical strain that should not be underestimated. You should therefore be fit and able to work under pressure, as it is not possible to simply take a break during a heart operation.
Precision is crucial for all heart-related procedures. This is particularly true for the treatment of small and delicate vessels and, of course, for any open heart surgery. The ability to work in a team is another important requirement, as you often work closely with teams from other areas of surgery and cardiology and have to recognise exactly who is responsible when.
Free information material
Studying medicine abroad 🎉
Order your info pack now, find out more about the Studying medicine abroad and get started as a medical student!





