☝️ The most important facts in brief
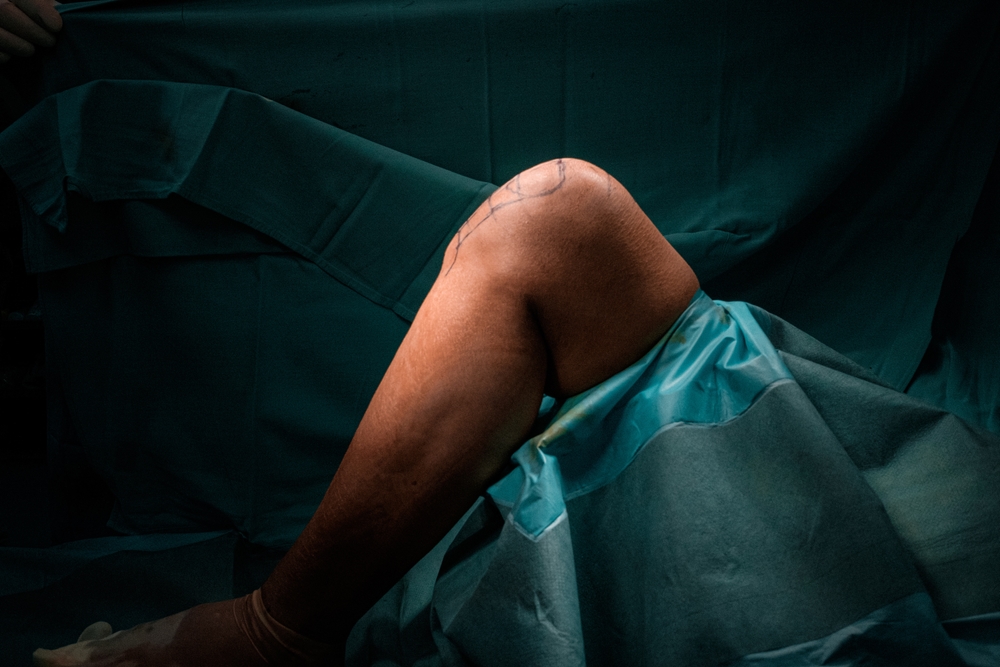
- Orthopaedic surgery focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, muscles and tendons.
- Further training for orthopaedic surgeons also includes further training in traumatology and trauma surgery. This means that you will also learn how to treat acute injuries to the musculoskeletal system, organs and soft tissue.
- To become a specialist in orthopaedic surgery and traumatology, you have to study human medicine for six years and then complete a further six years of training to become a specialist.
📖 Table of contents
Orthopaedic Surgery and trauma surgery are key medical specialisms. They include the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system as well as acute injuries in other areas. In this article, you will learn all about the tasks and specialisations that orthopaedic surgery and traumatology have to offer. We will show you how to become a specialist in orthopaedics and trauma surgery and what types of operations these doctors perform.
Are you interested in studying medicine?
We will be happy to advise you free of charge about your options for studying medicine, including advice on studying medicine in another EU country, which is fully recognised in Germany.
What is a specialist in orthopaedic surgery and traumatology?
A specialist in orthopaedics and trauma surgery primarily specialises in diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system. They treat bones, joints, tendons and ligaments. However, as a trauma surgeon, he can also deal with soft tissue injuries and provide patients with expert help in an emergency.
As part of planned operations, such a specialist can also perform operations on the spine and implant a joint replacement.
Your tasks as an orthopaedic and trauma surgeon
As an orthopaedic and trauma surgeon, you diagnose and treat diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system. Among other things, you can specialise in orthopaedic surgery and perform operations on various joints and bones.
Your tasks will also include aftercare and supporting those you have operated on in their rehabilitation.
What is the difference between trauma surgeons and orthopaedic surgeons?
Trauma surgeons treat acute injuries and traumas, often in the form of acute emergencies. Although trauma surgeons call in doctors from the relevant specialisms when necessary, they do not only treat the musculoskeletal system, but also injuries in all other areas.
Specialists in orthopaedic surgery, on the other hand, focus entirely on this area and also treat numerous chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis or meniscus problems.
Orthopaedic surgery - the fields of activity
Orthopaedic surgery covers a wide range of specific areas and correspondingly diverse options for diagnosis and treatment. From emergency medicine to endoprosthetics and sports orthopaedics, as a specialist in orthopaedic surgery you have numerous possible tasks. We would now like to introduce you to some of them in more detail.
Diagnostics of joint and bone diseases
Orthopaedic surgery centres on the diagnosis of bone and joint diseases. As a specialist, you specialise in the musculoskeletal system and treat the associated problems. In order to diagnose injuries, inflammations or other joint diseases, you will use imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI and CT.
Treatment of fractures and broken bones
An essential core task of traumatology is the treatment of fractures. The first step is to answer the usual questions about the type of fracture. Some fractures can simply be immobilised with a plaster cast. Other injuries need to be surgically repaired. Trauma specialists use plates, screws or nails to fix these fractures, which can be removed again once they have healed.
Endoprosthetics - joint replacement operations
Patients with severe joint diseases sometimes require joint replacement surgery. These aim to restore the function of the affected joint and thus make the patient more mobile again. Artificial joints can replace knee or hip joints, for example.
Arthroscopic surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used on the knee, shoulder and even the spine under certain conditions.
The procedure is mainly used in sports orthopaedics and trauma surgery. The orthopaedic surgery specialists only make small incisions and use special instruments to treat the affected joint.
Treatment with this method is less stressful than many other surgical therapies, so that recovery is faster.
Spinal surgery
Surgery on the spine requires special expertise, as an injury in this area can lead to paraplegia in the worst case scenario. Specialists who specialise in this area perform both minimally invasive and complex open operations. The aim of such operations is to restore mobility and relieve pain. In general, the functionality of the spine is an important factor in the overall quality of life of most patients.
Sports orthopaedics and surgery
The diagnosis and treatment of injuries caused by sporting activities is at the centre of this specialist area of orthopaedic surgery. Specialists in orthopaedics and trauma surgery treat both acute injuries and chronic conditions that prevent the affected area from bearing full weight.
Athletes frequently present to the sports orthopaedics department with knee and shoulder injuries. However, tendon and ligament injuries are also common and in some cases a case for foot surgery.
Orthopaedic tumour surgery
When tumours occur in the musculoskeletal system, this can be a case for a specialist in traumatology and orthopaedics. Such tumours can be direct tumours of the bone, but also invasive soft tissue tumours. Even tumours of the skin can in some cases restrict joint function and therefore require the expertise of an orthopaedic specialist, who then often works together with other specialists to restore the patient's health in the best possible way and without unnecessary restrictions.
Hand surgery
Operations on the hand are particularly complex, as numerous nerve tracts run through the hands, which must of course not be damaged during surgery. Hand surgery is therefore a specialised area within orthopaedic surgery.
Among other things, hand surgeons treat tendon ruptures, fractures and osteoarthritis of the hand, whose mobility and function can be crucial for the independence of those affected, as the hand is needed for many everyday activities.
Rehabilitation and aftercare
Proper aftercare is crucial for a smooth recovery. Surgery is therefore usually followed by targeted measures to support recovery and restore the function of affected joints quickly and as fully as possible.
Physiotherapy, occupational therapy and specialised training sessions help patients regain their mobility and strength. As a specialist in orthopaedic surgery, you will accompany the entire process to ensure optimal results.
Trauma surgery
A trauma surgeon treats acute injuries and trauma to the musculoskeletal system and sometimes other areas as well. He specialises in emergency care and surgical treatment, which is usually carried out as an acute case without lengthy planning.
Bone fractures, soft tissue injuries and complex multiple injuries are typical in this specialist area. Rapid and effective treatment is crucial for the health and recovery of accident victims.
Becoming a specialist in orthopaedics and traumatology - the training programme
To become a specialist in orthopaedics and traumatology, you need at least 11 years after completing your A-levels. First you have to Study medicine and take your state examination. This is followed by further training to become a specialist in orthopaedics and trauma surgery. We would now like to take a closer look at these two key stages on the path to becoming a qualified specialist.
Medical studies
The six-year medical degree forms the basis for your career as a doctor, regardless of which specialisation you wish to pursue after your studies. Whether Munich, Kiel or Heidelberg: first you have to get a place at a university. Unfortunately, this is anything but easy in the human medicine degree programme, which is why many A-level students decide to study abroad in order to realise their dream of becoming a doctor. We are happy to support you with this if required.
Specialist training
After successfully completing your studies, you can start your 5-year training programme to become a specialist in orthopaedics and trauma surgery. You will deepen the basic knowledge of orthopaedic surgery and traumatology that you have already acquired during your studies. You will also acquire a great deal of specific expertise on the individual joints and emergency medicine.
Once you have successfully completed all parts of your further training and successfully passed the examinations specified in the further training regulations, you will be a specialist in orthopaedic surgery and traumatology and can apply for relevant positions.
Opening your own practice - requirements and prospects
To open your own practice for orthopaedics and traumatology, you must fulfil various requirements: You must have successfully completed your specialist training and therefore be a qualified specialist in traumatology and orthopaedic surgery.
Bear in mind that you will either have to take over an existing specialist practice for a sometimes high price or invest in the furnishings and modern equipment yourself.
A good location, ideally in an easily accessible city such as Munich, Berlin or Hamburg, will improve your prospects. However, these locations are generally also significantly more expensive. In the long term, however, you can earn an excellent income with your own practice, which is why it can be worthwhile to become a self-employed specialist in orthopaedic surgery and traumatology.
Free information material
Studying medicine abroad 🎉
Order your info pack now, find out more about the Studying medicine abroad and get started as a medical student!





