☝️ The most important facts in brief
- Infectiology is a speciality of internal medicine.
- Dealing with serious infectious diseases such as HIV, tuberculosis and pneumonia is part of an infectiologist's everyday work.
- The work in infectiology includes diagnostics, therapy and the management of infections.
- Infectiologists are often requested by doctors from other specialist areas for consultations when special expertise is required.
📖 Table of contents
Infectiologists are medical specialists who specialise in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of infectious diseases. Their speciality, infectiology, is part of internal medicine. They provide patients with advice and support in clinics, outpatient clinics and also at AIDS-Hilfe. We explain how you can become an infectiologist, the tasks involved and how you can help people in this profession.
Are you interested in studying medicine?
We will be happy to advise you free of charge about your options for studying medicine, including advice on studying medicine in another EU country, which is fully recognised in Germany.
What is infectiology?
Infectiology is a branch of internal medicine that deals with infectious diseases. Infectiologists diagnose, treat and manage a wide range of infectious diseases. Clinical infectiology plays a central role in medical care and research. Essentially, the work of an infectiologist primarily covers the diagnostic and therapeutic areas. This applies to both the outpatient clinic and the hospital.
Diagnostics
In infectiology, various methods are used to precisely identify pathogens. Analyses in the microbiology laboratory are an integral part of this. The aim is to be able to identify infections as quickly and correctly as possible so that the correct treatment can then be initiated.
Therapy
As an infectious diseases doctor, you will develop customised treatment plans for your patients. You will also be responsible for advising doctors from other departments when they reach the limits of their expertise.
Research and teaching
Other important areas are research and the training of future doctors and specialists. Research into infectious diseases and the development of modern therapies is significantly supported by the German Society for Infectiology in Berlin. In addition to working in the clinic, there is also the opportunity to obtain the title "Dr. Med." through a doctoral thesis. through a doctoral thesis. If you continue your academic career, you can even become "Prof. Dr Med.". This includes both research and teaching medical students.
Infectiology plays an important role in the prevention of antibiotic resistance
It is a growing threat in medicine that an antibiotic is often no longer effective because the bacteria have developed resistance to it. Infectiology plays a crucial role in preventing this resistance: The concept of "antibiotic stewardship" develops therapies in which antibiotics are used in a targeted manner. This helps the patient without causing the dreaded problems.
How to become a specialist in internal medicine and infectiology
Specialists in infectiology must first complete a degree in medicine. After the state examination, you can then complete further training to become a specialist in internal medicine, which takes around 5 years. During this time, you will acquire comprehensive knowledge about the diagnosis and treatment of infections, as well as other skills.
You can then specialise in infectiology in a one-year further training course. The title "Specialist in Internal Medicine and Infectiology" has been an independent specialist title since 2021. You do not need the title of Dr med to become an infectiologist. However, this can significantly improve your career opportunities in clinical practice and research. If you then even get the chance to become a professor, the title of "Prof. Dr med" will be within reach.
Which infectious diseases do infectiologists deal with?
As an infectiologist, you will deal with a variety of infectious diseases. These range from everyday to rare and complex cases. Here are some examples of diseases that the infectiology team often has to deal with:
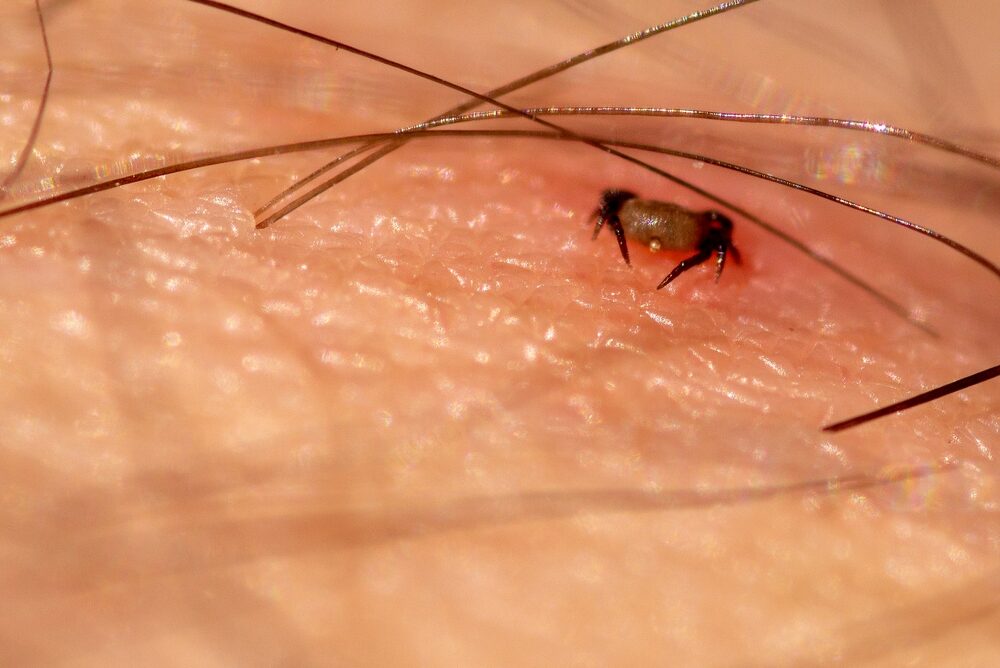
Lyme disease
Lyme borreliosis is transmitted by ticks. Infectiologists diagnose this disease based on symptoms such as fever and skin rash and initiate the appropriate treatment.
COVID 19
The COVID-19 pandemic has once again emphasised the importance of infectiology. In particular, patients who require treatment in hospital benefit from the in-depth expertise of infectiologists.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammatory liver disease that occurs in various forms. In many cases, treatment includes antiviral medication and regular check-ups at the clinic.
HIV
The treatment of HIV and AIDS is one of the core tasks of infectiology. Specialised teams in clinics offer comprehensive counselling and therapy to improve the quality of life of HIV patients. AIDS is still not curable, but thanks to modern medication, patients today have an almost normal life expectancy despite HIV.
Sexually transmitted diseases
Syphilis, gonorrhoea and other sexually transmitted infections are still widespread. In many regions, the healthcare system has a dedicated department for this, which not only deals with diagnosis and treatment, but also makes an important contribution to prevention online, by email and on site.
Other reasons why patients present to the infectiology department
In many cases, patients come after travelling to have unclear illnesses clarified. Depending on the symptoms and location of the trip, it sometimes makes sense to consult a specialist in tropical medicine in such cases. Tuberculosis also continues to occur in Germany. Other reasons why patients are referred to the infectiology department include
- Unclear fever
- Tendency to infections
- Upcoming trip to risk areas (also possibly a case for tropical medicine)
- Immunosuppression
Free information material
Studying medicine abroad 🎉
Order your info pack now, find out more about the Studying medicine abroad and get started as a medical student!





